tomcat 的源码,看了之后会让人感觉它的设计是如此巧妙,大部分核心组件都是经过高度抽象。
这也是第二次看源码了,第一次看源码的时候感觉就像人入大海不知道 从何看起,花了很多时间也只了解了tomcat 里 有这几个类 Server、Service、endpoint、Host、Connector ,后来恰巧看到了《tomcat内核设计剖析》(这部书是基于tomcat7写的,差别不是太大) 这本书后,对tomcat在组件设计即架构方目已经代码的迭代跟新后 是如此的清晰、巧妙的印象更深了,所有后来有时间后就又开始学习tomcat的源码。
我是用的 tomcat 源码版本是 apache-tomcat-8.5.38-src
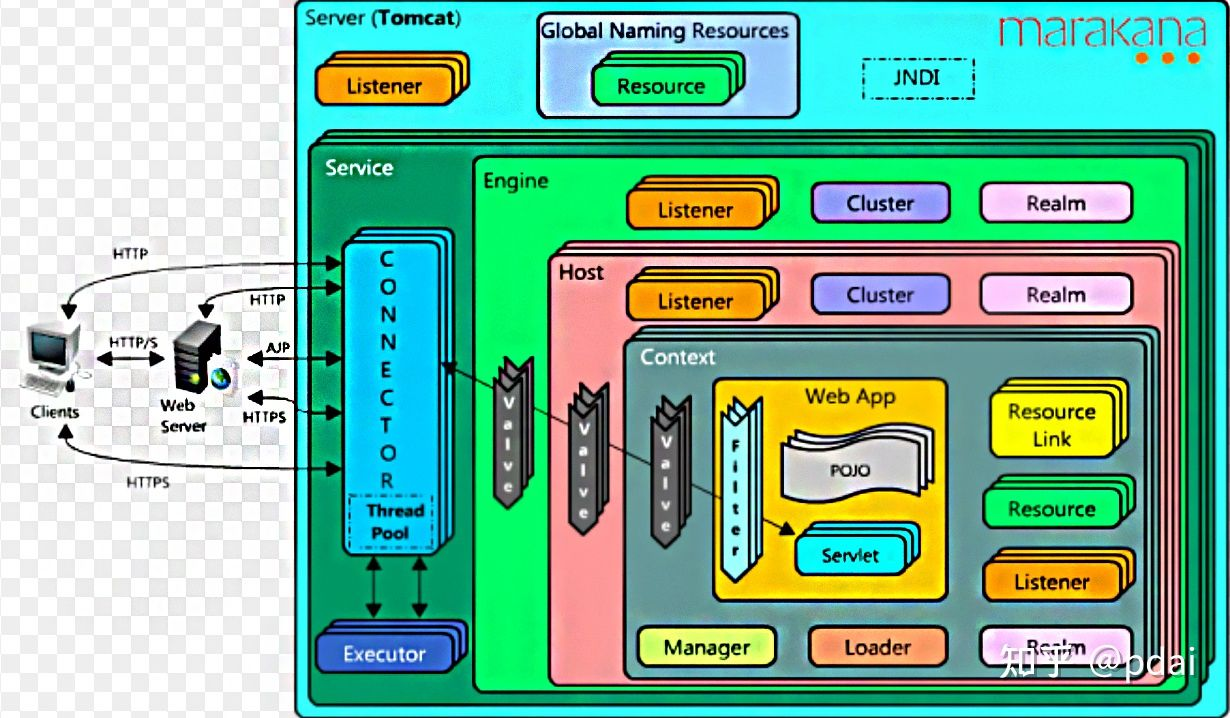
本文主要了解 tomcat的启动到组件的初始化在查看源码前,需要看一下tomcat 的架构图,对tomcat 有哪些组件 ,以及组件与组件直接的关系是怎么样的有一个大概了解,这样对我们查看源码有一定帮助,不至于太过迷茫。
首选看 org.apache.catalina.startup.Bootstrap main
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 elif [ "$1 " = "run" ]; then shift if [ "$1 " = "-security" ] ; then if [ $have_tty -eq 1 ]; then echo "Using Security Manager" fi shift eval exec "\"$_RUNJAVA \"" "\"$LOGGING_CONFIG \"" $LOGGING_MANAGER $JAVA_OPTS $CATALINA_OPTS \ -D$ENDORSED_PROP ="\"$JAVA_ENDORSED_DIRS \"" \ -classpath "\"$CLASSPATH \"" \ -Djava.security.manager \ -Djava.security.policy=="\"$CATALINA_BASE /conf/catalina.policy\"" \ -Dcatalina.base="\"$CATALINA_BASE \"" \ -Dcatalina.home="\"$CATALINA_HOME \"" \ -Djava.io.tmpdir="\"$CATALINA_TMPDIR \"" \ org.apache.catalina.startup.Bootstrap "$@ " start else eval exec "\"$_RUNJAVA \"" "\"$LOGGING_CONFIG \"" $LOGGING_MANAGER $JAVA_OPTS $CATALINA_OPTS \ -D$ENDORSED_PROP ="\"$JAVA_ENDORSED_DIRS \"" \ -classpath "\"$CLASSPATH \"" \ -Dcatalina.base="\"$CATALINA_BASE \"" \ -Dcatalina.home="\"$CATALINA_HOME \"" \ -Djava.io.tmpdir="\"$CATALINA_TMPDIR \"" \ org.apache.catalina.startup.Bootstrap "$@ " start fi
还有就是在我们启动 tomcat 后可以 用 jps 命令查看启动的tomcat 进程的名字 Bootstrap
下面我们看看 Bootstrap main方法
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 public static void main (String args[]) if (daemon == null ) { Bootstrap bootstrap = new Bootstrap(); try { bootstrap.init(); } catch (Throwable t) { handleThrowable(t); t.printStackTrace(); return ; } daemon = bootstrap; } else { Thread.currentThread().setContextClassLoader(daemon.catalinaLoader); } try { String command = "start" ; if (args.length > 0 ) { command = args[args.length - 1 ]; } if (command.equals("startd" )) { args[args.length - 1 ] = "start" ; daemon.load(args); daemon.start(); } else if (command.equals("stopd" )) { args[args.length - 1 ] = "stop" ; daemon.stop(); } else if (command.equals("start" )) { daemon.setAwait(true ); daemon.load(args); daemon.start(); if (null == daemon.getServer()) { System.exit(1 ); } } else if (command.equals("stop" )) { daemon.stopServer(args); } else if (command.equals("configtest" )) { daemon.load(args); if (null == daemon.getServer()) { System.exit(1 ); } System.exit(0 ); } else { log.warn("Bootstrap: command \"" + command + "\" does not exist." ); } } catch (Throwable t) { if (t instanceof InvocationTargetException && t.getCause() != null ) { t = t.getCause(); } handleThrowable(t); t.printStackTrace(); System.exit(1 ); } }
我们主要查看 这里面的两个方法
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 else if (command.equals("start" )) { daemon.setAwait(true ); daemon.load(args); daemon.start(); if (null == daemon.getServer()) { System.exit(1 ); } }
load方法代码如下
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 private void load (String[] arguments) throws Exception { String methodName = "load" ; Object param[]; Class<?> paramTypes[]; if (arguments==null || arguments.length==0 ) { paramTypes = null ; param = null ; } else { paramTypes = new Class[1 ]; paramTypes[0 ] = arguments.getClass(); param = new Object[1 ]; param[0 ] = arguments; } Method method = catalinaDaemon.getClass().getMethod(methodName, paramTypes); if (log.isDebugEnabled()) log.debug("Calling startup class " + method); method.invoke(catalinaDaemon, param); }
catalinaDaemon 是通过反射加载的,我们可以看看 catalinaDaemon这个变量是在什么地方进行赋值的 ,我们在文件里搜一下发现是 Bootstrap.init()方法中进行赋值的
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 public void init () throws Exception initClassLoaders(); Thread.currentThread().setContextClassLoader(catalinaLoader); SecurityClassLoad.securityClassLoad(catalinaLoader); if (log.isDebugEnabled()) log.debug("Loading startup class" ); Class<?> startupClass = catalinaLoader.loadClass("org.apache.catalina.startup.Catalina" ); Object startupInstance = startupClass.getConstructor().newInstance(); if (log.isDebugEnabled()) log.debug("Setting startup class properties" ); String methodName = "setParentClassLoader" ; Class<?> paramTypes[] = new Class[1 ]; paramTypes[0 ] = Class.forName("java.lang.ClassLoader" ); Object paramValues[] = new Object[1 ]; paramValues[0 ] = sharedLoader; Method method = startupInstance.getClass().getMethod(methodName, paramTypes); method.invoke(startupInstance, paramValues); catalinaDaemon = startupInstance; }
catalinaDaemon = startupInstance; 我们可以看到 这个类其实就是 org.apache.catalina.startup.Catalina
那调用 load方法就是通反射调用 org.apache.catalina.startup.Catalina 的load方法 可以看看 org.apache.catalina.startup.Catalina 里面有没有load方法
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 public void load () if (loaded) { return ; } loaded = true ; long t1 = System.nanoTime(); ... }
还真有,上面还有一个注释,这就很明显了 。
我们可以看看这个方法里面的具体内容
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 public void load () if (loaded) { return ; } loaded = true ; long t1 = System.nanoTime(); initDirs(); initNaming(); Digester digester = createStartDigester(); InputSource inputSource = null ; InputStream inputStream = null ; File file = null ; try { try { file = configFile(); inputStream = new FileInputStream(file); inputSource = new InputSource(file.toURI().toURL().toString()); } catch (Exception e) { if (log.isDebugEnabled()) { log.debug(sm.getString("catalina.configFail" , file), e); } } if (inputStream == null ) { try { inputStream = getClass().getClassLoader() .getResourceAsStream(getConfigFile()); inputSource = new InputSource (getClass().getClassLoader() .getResource(getConfigFile()).toString()); } catch (Exception e) { if (log.isDebugEnabled()) { log.debug(sm.getString("catalina.configFail" , getConfigFile()), e); } } } if (inputStream == null ) { try { inputStream = getClass().getClassLoader() .getResourceAsStream("server-embed.xml" ); inputSource = new InputSource (getClass().getClassLoader() .getResource("server-embed.xml" ).toString()); } catch (Exception e) { if (log.isDebugEnabled()) { log.debug(sm.getString("catalina.configFail" , "server-embed.xml" ), e); } } } if (inputStream == null || inputSource == null ) { if (file == null ) { log.warn(sm.getString("catalina.configFail" , getConfigFile() + "] or [server-embed.xml]" )); } else { log.warn(sm.getString("catalina.configFail" , file.getAbsolutePath())); if (file.exists() && !file.canRead()) { log.warn("Permissions incorrect, read permission is not allowed on the file." ); } } return ; } try { inputSource.setByteStream(inputStream); digester.push(this ); digester.parse(inputSource); } catch (SAXParseException spe) { log.warn("Catalina.start using " + getConfigFile() + ": " + spe.getMessage()); return ; } catch (Exception e) { log.warn("Catalina.start using " + getConfigFile() + ": " , e); return ; } } finally { if (inputStream != null ) { try { inputStream.close(); } catch (IOException e) { } } } getServer().setCatalina(this ); getServer().setCatalinaHome(Bootstrap.getCatalinaHomeFile()); getServer().setCatalinaBase(Bootstrap.getCatalinaBaseFile()); initStreams(); try { getServer().init(); } catch (LifecycleException e) { if (Boolean.getBoolean("org.apache.catalina.startup.EXIT_ON_INIT_FAILURE" )) { throw new java.lang.Error(e); } else { log.error("Catalina.start" , e); } } long t2 = System.nanoTime(); if (log.isInfoEnabled()) { log.info("Initialization processed in " + ((t2 - t1) / 1000000 ) + " ms" ); } }
可以看出,tomcat的方法命名还是很清晰的,
initDirs(); 初始化目录
digester.parse(inputSource); 解析 tomcat配置文件 即 Server.xml 这里用的是apache 的digester 解析的
getServer().setCatalina(this);
这几个是设置Server 文件路径 的 ,看名字就能猜到
getServer().init();
这个就明显了初始化 记住,这个方法是 Bootstrap.load()方法中调用的
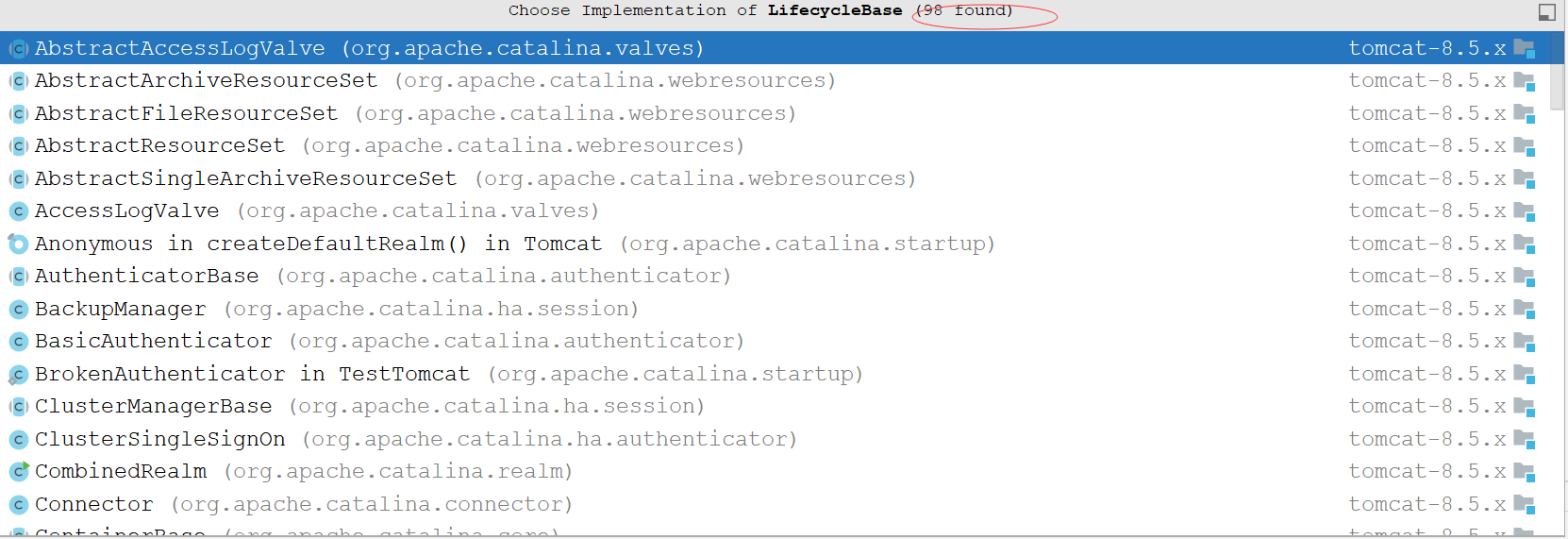
idea Ctrl+Alt+B getServer().init(); 方法发现我们跳到 了 org.apache.catalina.util.LifecycleBase
这个类是tomcat 抽象出来的 一个生命周期接口 很多tomcat 的组件都是 实现的这个接口 Ctrl+Alt+B 我们可以看到这个类的实现在tomcat中有98个
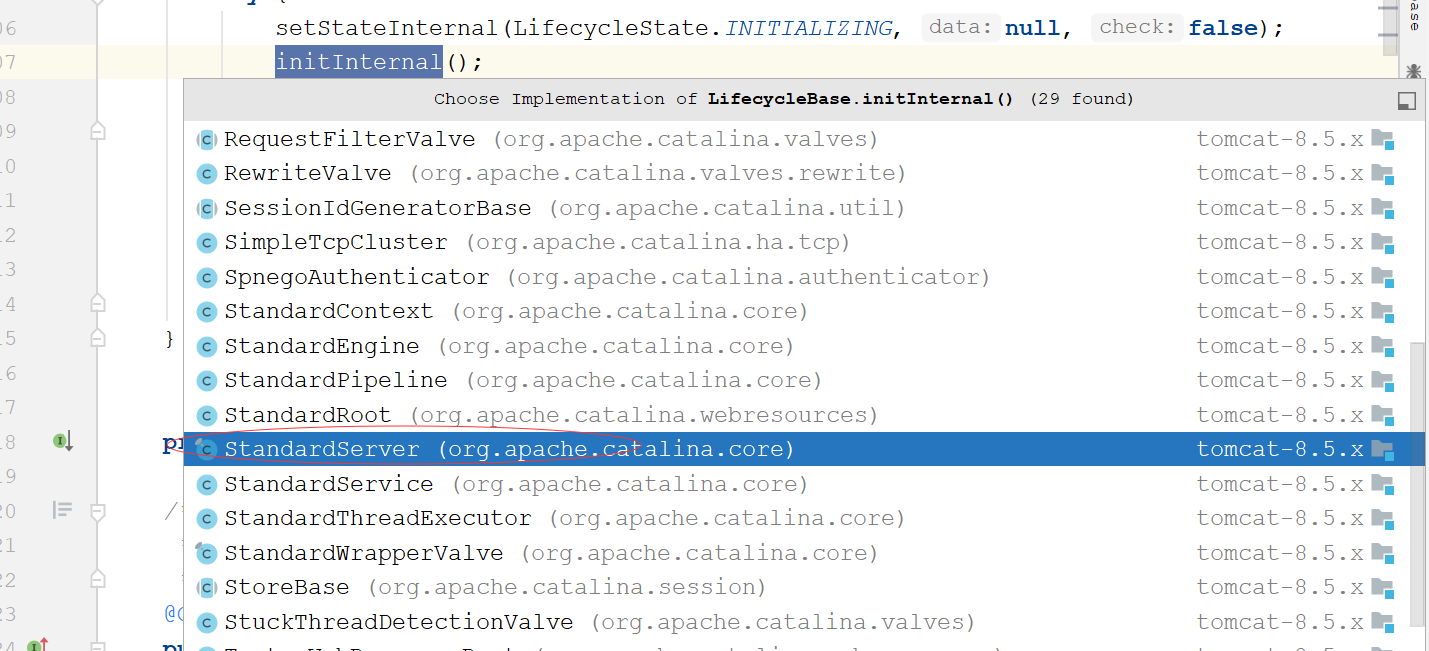
在 org.apache.catalina.util.LifecycleBase *init()*方法中
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 @Override public final synchronized void init () throws LifecycleException if (!state.equals(LifecycleState.NEW)) { invalidTransition(Lifecycle.BEFORE_INIT_EVENT); } try { setStateInternal(LifecycleState.INITIALIZING, null , false ); initInternal(); setStateInternal(LifecycleState.INITIALIZED, null , false ); } catch (Throwable t) { ExceptionUtils.handleThrowable(t); setStateInternal(LifecycleState.FAILED, null , false ); throw new LifecycleException( sm.getString("lifecycleBase.initFail" ,toString()), t); } }
我们可以看到有一个 initInternal()方法 在这个方法上使用 Ctrl+Alt+B找到 org.apache.catalina.core.StandardServer 这个类,因为之前我们是通过 getServer().init(); 方法跳过去的而在 getServer() 返回的是一个 Server 接口 ,Server接口的实现只有一个 org.apache.catalina.core.StandardServe
在 org.apache.catalina.core.StandardServer initInternal()
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 protected void initInternal () throws LifecycleException super .initInternal(); onameStringCache = register(new StringCache(), "type=StringCache" ); MBeanFactory factory = new MBeanFactory(); factory.setContainer(this ); onameMBeanFactory = register(factory, "type=MBeanFactory" ); globalNamingResources.init(); if (getCatalina() != null ) { ClassLoader cl = getCatalina().getParentClassLoader(); while (cl != null && cl != ClassLoader.getSystemClassLoader()) { if (cl instanceof URLClassLoader) { URL[] urls = ((URLClassLoader) cl).getURLs(); for (URL url : urls) { if (url.getProtocol().equals("file" )) { try { File f = new File (url.toURI()); if (f.isFile() && f.getName().endsWith(".jar" )) { ExtensionValidator.addSystemResource(f); } } catch (URISyntaxException e) { } catch (IOException e) { } } } } cl = cl.getParent(); } } for (int i = 0 ; i < services.length; i++) { services[i].init(); } }
以此类推 org.apache.catalina.core.StandardService 的 initInternal()
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 @Override protected void initInternal () throws LifecycleException super .initInternal(); if (engine != null ) { engine.init(); } for (Executor executor : findExecutors()) { if (executor instanceof JmxEnabled) { ((JmxEnabled) executor).setDomain(getDomain()); } executor.init(); } mapperListener.init(); synchronized (connectorsLock) { for (Connector connector : connectors) { try { connector.init(); } catch (Exception e) { String message = sm.getString( "standardService.connector.initFailed" , connector); log.error(message, e); if (Boolean.getBoolean("org.apache.catalina.startup.EXIT_ON_INIT_FAILURE" )) throw new LifecycleException(message); } } } }
到这里可以看到 Connector 是可以有多个的和一开始的 tomcat 架构图中 各个组件 是一一对应的关系
对于tomcat大部分组件都可以 在架构图上找到并且以这种方式进行查看代码。